The Ultimate Guide to the Three Financial Statements
How to Cope With Anxiety
April 24, 202015 Best Sobriety Podcasts to Support Recovery
April 27, 2020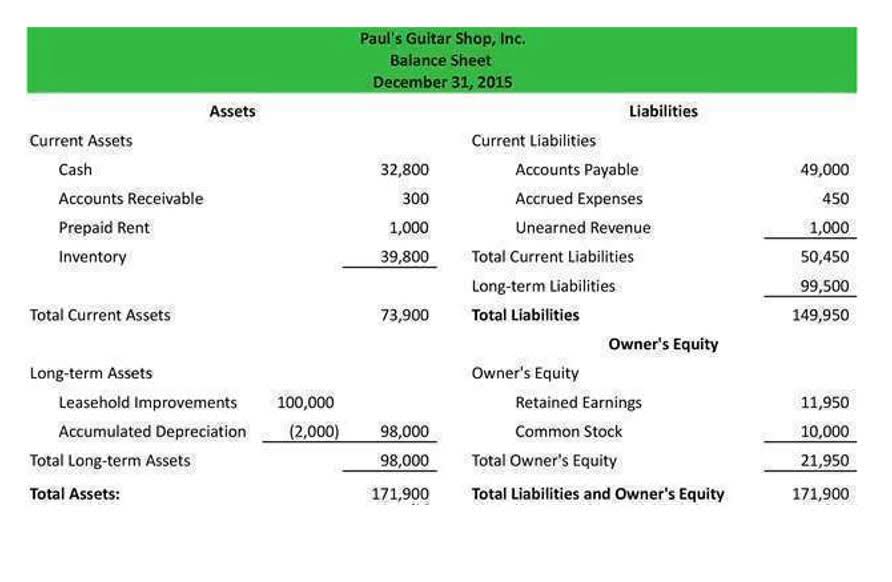
Expenses are decreases in economic benefit during the accounting period in the form of a decrease in asset or an increase Accounting Security in liability that result in decrease in equity, other than distribution to owners. Revenues refer to the amounts earned from the company’s ordinary course of business such as professional fees or service revenue for service companies and sales for merchandising and manufacturing concerns. Personal financial statements give you the tools to monitor your spending and increase your net worth. Also, in business—and accounting in particular—it is necessary to distinguish the business entity from the individual owner(s). Accountants should record only business transactions in business records. Another distinguishing feature between liabilities and equity is that the return on equity (e.g., dividends and capital gains) is primarily based on the business performance.

Losses
- You only enter the transactions once rather than show the impact of the transactions on two or more accounts.
- It is useful for a variety of stakeholders, including shareholders, creditors, customers, suppliers, and the organization itself.
- Only after debts are settled are shareholders entitled to any of the company’s assets to attempt to recover their investment.
- With liabilities, this is obvious – you owe loans to a bank, or repayment of bonds to holders of debt, etc.
- Thus, equity is not only a critical component of the accounting equation but also an essential indicator of a company’s financial health and operational effectiveness.
- The ability to understand financial statements is a significant benefit to investors.
More specifically, we are accounting for the value of distributions to the owners and net loss, if any. Owner contributions, also known as capital contributions or investments, further enhance the equity section of unearned revenue the accounting equation. In essence, the accounting equation connects the resources a business has at its disposal with the claims against those resources.
- The balance sheet and the P&L statement are both essential financial documents but serve different purposes and provide other information.
- Recall that current assets and current liabilities are amounts generally settled in one year or less.
- Costly items, such as vehicles, equipment, and computer systems, are not expensed, but are depreciated or written off over the life expectancy of the item.
- These revenues will be balanced on the assets side, appearing as cash, investments, inventory, or other assets.
- The balance sheet is a very important financial statement for many reasons.
Assets, liabilities, and capital
It is useful for assessing a company’s financial health, net worth, liquidity, and book value. Investors, creditors, and other stakeholders can use the balance sheet to make informed decisions about a company’s financial standing. Similar to the previous example for the mechanic, a credit sale, however, would be treated differently under each of these types of accounting. Under the cash basis of accounting, a credit sale would not be recorded in the financial statements until the cash is received, under terms stipulated by the seller. For example, assume on April 1 a landscaping business provides $500 worth of services to one of its customers. Under the cash basis of accounting, the revenue would not be recorded until May 16, when the cash was received.
- This line item includes all of the company’s intangible fixed assets, which may or may not be identifiable.
- The Liabilities part of the equation is usually comprised of accounts payable that are owed to suppliers, a variety of accrued liabilities, such as sales taxes and income taxes, and debt payable to lenders.
- Current liabilities are due within one year and are listed in order of their due date.
- Assets include any real estate owned or controlled by the business but also include other resources such as cash, inventory, and receivables that increase the worth of a business.
- As you can see, shareholder’s equity is the remainder after liabilities have been subtracted from assets.
The Importance of a Balance Sheet
Let’s now explore the difference between the cash basis and accrual basis of accounting using an expense. Assume a business purchases $160 worth of printing supplies a statement that shows the relationship between an individuals assets, liabilities, and equity. from a supplier (vendor). Similar to a sale, a purchase of merchandise can be paid for at the time of sale using cash (also a check or credit card) or at a later date (on account). A purchase paid with cash at the time of the sale would be recorded in the financial statements under both cash basis and accrual basis of accounting. It makes sense because the business received the printing supplies from the supplier and paid the supplier at the same time.
- It lists your assets (what you own) and liabilities (what you owe), which allows you to calculate your net worth.
- The accrual method is also discussed in greater detail in Explain the Steps within the Accounting Cycle through the Unadjusted Trial Balance.
- At a general level, this means that whenever there is a recordable transaction, the choices for recording it all involve keeping the accounting equation in balance.
- Balance sheets give you a snapshot of all the assets, liabilities and equity that your company has on hand at any given point in time.
- Individual transactions which result in income and expenses being recorded will ultimately result in a profit or loss for the period.
Types of Assets and Liabilities

Now let’s look a closer look at each of these basic elements of accounting. Get free guides, articles, tools and calculators to help you navigate the financial side of your business with ease. This change must be offset by a $500 increase in Total Liabilities or Total Equity. The formula defines the relationship between a business’s Assets, Liabilities and Equity.

The Accounting Equation and the Classified Balance Sheet

The classified balance sheet shows the financial state of a company as of a specific point in time. The classified balance sheet is prepared in sections that align with the accounting equation. The third financial statement created is the balance sheet, which shows the company’s financial position on a given date. If your business has more than one owner, you split your equity among all the owners. Include the value of all investments from any stakeholders in your equity as well. Subtract your total assets from your total liabilities to calculate your business equity.

